How to manage the migrant crisis
A European problem demands a common, coherent EU policy. Let refugees in, but regulate the flow
Reffugees are reasonable people in desperate circumstances. Life for many of the 1m-odd asylum-seekers who have fled Syria, Iraq, Afghanistan and other war-torn countries for Europe in the past year has become intolerable. Europe is peaceful, rich and accessible. Most people would rather not abandon their homes and start again among strangers. But when the alternative is the threat of death from barrel-bombs and sabre-wielding fanatics, they make the only rational choice.
The flow of refugees would have been manageable if European Union countries had worked together, as Angela Merkel, Germany’s chancellor, has always wished (and The Economist urged). Instead Germany and Sweden have been left to cope alone. Today their willingness to do so is exhausted. Unless Europe soon restores order, political pressure will force Mrs Merkel to clamp down unilaterally, starting a wave of border closures (see article). More worrying, the migrant crisis is feeding xenophobia and political populism. The divisive forces of right-wing nationalism have already taken hold in parts of eastern Europe. If they spread westward into Germany, France and Italy then the EU could tear itself apart.
Read the full article on The Economist website
Related Articles
Stop targeting humanitarian workers
03/08/2017. Humanitarian workers have to balance the risks they are facing with the life-saving impact of their humanitarian work.
Humanitarian promises instead of political solution
02/04/2016. Donors pledged to give more than $ 10 billion by 2020 to help Syrians
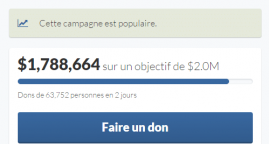
Ben Stiller and Social Media Stars Launch ‘Love Army’ to Aid in Somali Crisis
03/22/2017. Celebrities have banded together for a viral fundraising campaign to help offset the humanitarian crisis in Somalia, raising more than $2 million in less a week.